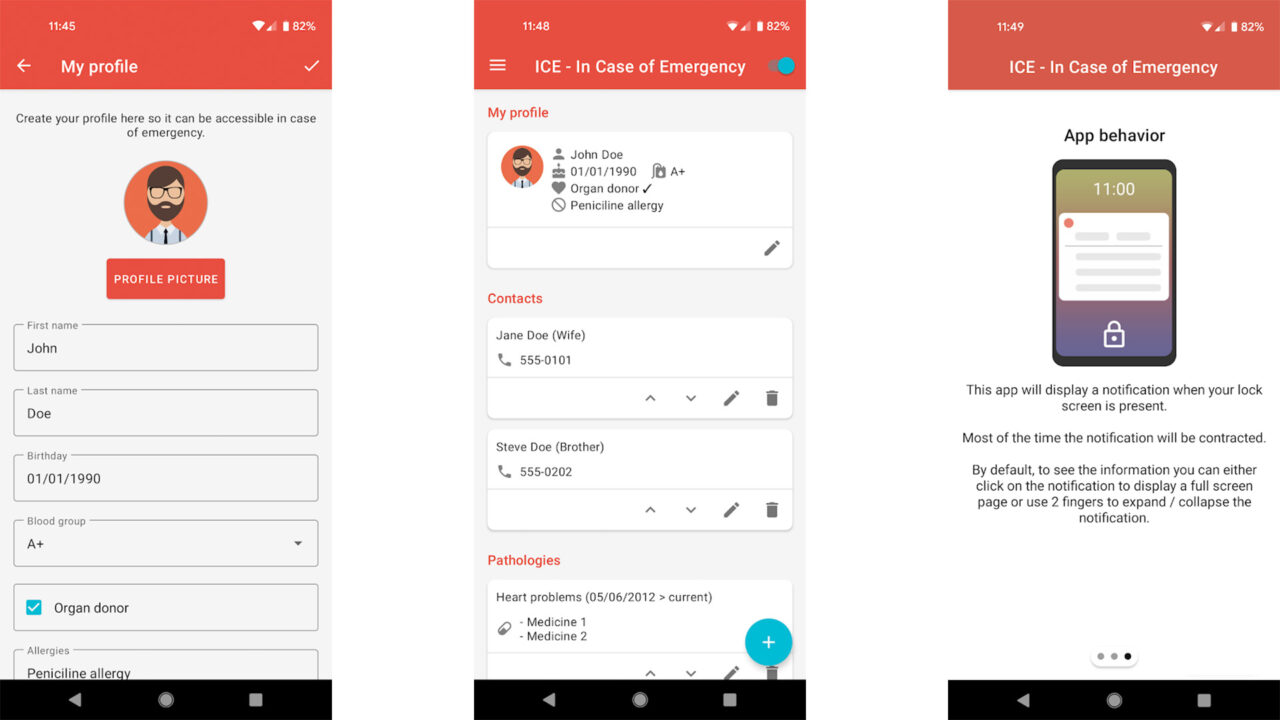
Top Food Delivery Apps Americans Love in 2025 takes center stage as the food delivery landscape evolves with technology and consumer preferences. As dining habits shift towards convenience and speed, numerous food delivery applications are vying for the attention of American consumers. This exploration delves into the most popular and effective platforms that not only cater to a diverse range of culinary tastes but also adapt to the dynamic needs of users in an increasingly digital world.
The rise of these apps reflects broader trends in dining, including the growing preference for on-demand services and the fusion of various cuisines. As we analyze the key features, customer experiences, and technological innovations driving these platforms, it becomes evident how they shape the modern dining experience in 2025.
Climate change represents one of the most significant challenges facing the global environment today. The term encompasses a broad spectrum of alterations in the Earth’s climate, primarily driven by human activities such as the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes. These actions have led to an increase in greenhouse gases (GHGs) in the atmosphere, causing global temperatures to rise.
This article delves into how these alterations have profound implications for biodiversity, the interconnected web of life consisting of various species and ecosystems.
The Relationship Between Climate Change and Biodiversity
Biodiversity refers to the variety of life found in a specific area, encompassing species diversity, genetic diversity, and ecosystem diversity. A stable and diverse biological community is essential for maintaining ecosystem services, which include pollination, nutrient cycling, and regulation of climate. However, climate change poses a significant threat to these ecosystems through various mechanisms, including habitat alteration, species extinction, and changes in species distribution.
Habitat Loss and Alteration
One of the most immediate effects of climate change is the alteration of habitats. As global temperatures rise, many ecosystems are experiencing shifts in their geographic ranges. For instance, forests, wetlands, and coral reefs are particularly vulnerable to changes in temperature and precipitation patterns. As habitats change or disappear, the species that rely on them may be forced to adapt, migrate, or face extinction.
Species Extinction
Species extinction is perhaps the most dire consequence of climate change. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), a significant percentage of plant and animal species are at risk of extinction due to climate change. Factors such as changes in temperature, sea level rise, and increased frequency of extreme weather events can disrupt breeding, feeding, and migration patterns.
For example, polar bears are heavily impacted by melting ice caps, which diminish their hunting grounds and threaten their survival.
Shifts in Species Distribution, Top Food Delivery Apps Americans Love in 2025
Another major impact of climate change is the shift in species distribution. As temperatures warm, many species are moving toward higher altitudes and latitudes in search of more suitable climates. This migration can lead to competition for resources, changes in predator-prey dynamics, and the potential introduction of invasive species into new ecosystems. For example, the distribution of various bird species has already shifted, leading to mismatches in their breeding seasons and food availability.

The Effects on Ecosystem Services
The decline in biodiversity due to climate change has significant implications for ecosystem services that human populations rely on. Ecosystem services are the benefits that humans derive from nature, including clean water, air purification, and food production. A decline in biodiversity can compromise these services, leading to increased vulnerability to natural disasters, food insecurity, and public health challenges.
Food Production
A diverse ecosystem is crucial for agriculture as it supports pollinators and natural pest control mechanisms. Climate change threatens to alter growing seasons, impact crop yields, and affect food supply chains. Crop species that are not genetically diverse are more susceptible to pests and diseases, which could exacerbate food insecurity. For example, the changing climate may lead to reduced yields of staple crops such as wheat and rice, directly impacting global food supply.
Water Resources
Freshwater ecosystems are also at risk due to climate change. Alterations in precipitation patterns can lead to water scarcity in some regions while causing flooding in others. These changes can affect the availability of clean drinking water, impact agricultural irrigation, and disrupt aquatic habitats. The decline of healthy freshwater ecosystems can reduce water quality, leading to health issues for human populations and wildlife alike.
Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies
Addressing the impact of climate change on biodiversity requires coordinated global efforts focused on both mitigation and adaptation strategies. Mitigation involves reducing the sources of greenhouse gas emissions, while adaptation entails adjusting management and conservation strategies to cope with the changing climate.
Conservation Efforts
Conservation strategies must evolve to incorporate climate change considerations. Protected areas may need to be expanded or relocated to accommodate shifting species distributions. Additionally, restoration ecology can play a role in enhancing ecosystem resilience, allowing ecosystems to better withstand climate stresses. Engaging local communities in conservation efforts can foster stewardship and enhance the effectiveness of these strategies.
Policy and Legislation
Government policies play a critical role in addressing climate change and its impact on biodiversity. International agreements such as the Paris Agreement aim to limit global warming and promote sustainable development. National and local policies must support initiatives that prioritize biodiversity conservation, such as sustainable land-use planning, habitat protection, and the promotion of renewable energy sources.
The Role of Individuals: Top Food Delivery Apps Americans Love In 2025
While large-scale initiatives are essential, individual actions can also contribute to mitigating climate change and protecting biodiversity. Simple steps, such as reducing energy consumption, supporting local and sustainable agriculture, and participating in conservation programs, can collectively make a significant impact. Education and awareness campaigns can empower individuals to take action and advocate for policies that prioritize environmental sustainability.
Conclusion
The intersection of climate change and biodiversity is a pressing issue that requires immediate attention. The loss of biodiversity not only threatens ecosystems but also jeopardizes the services that sustain human life. By understanding the complex relationships between climate change and biodiversity, we can develop effective strategies to mitigate the impacts of climate change and promote the conservation of our planet’s rich biological heritage.
Collaborative efforts among scientists, policymakers, communities, and individuals are crucial to forging a sustainable future where biodiversity thrives alongside human development.