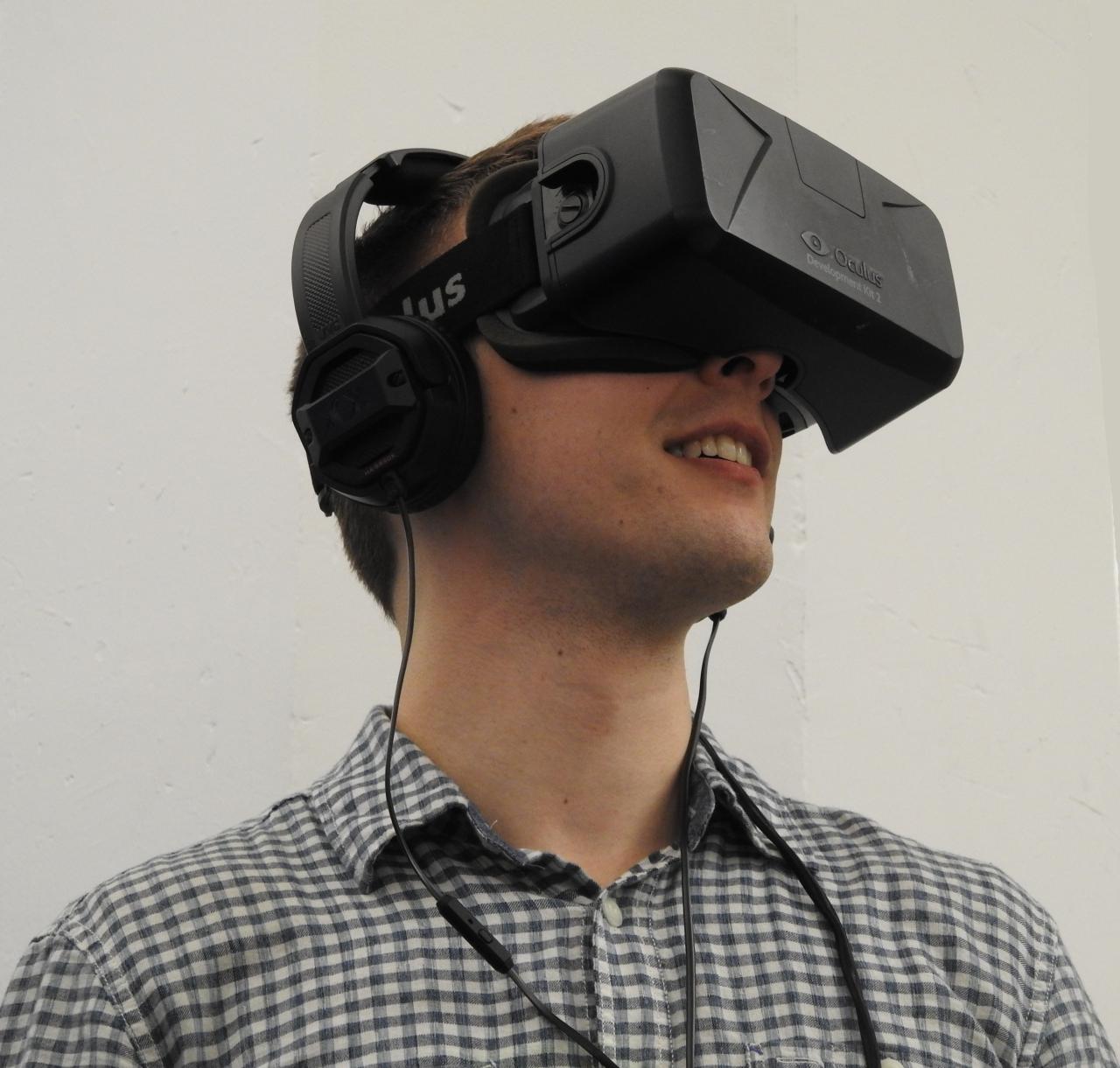
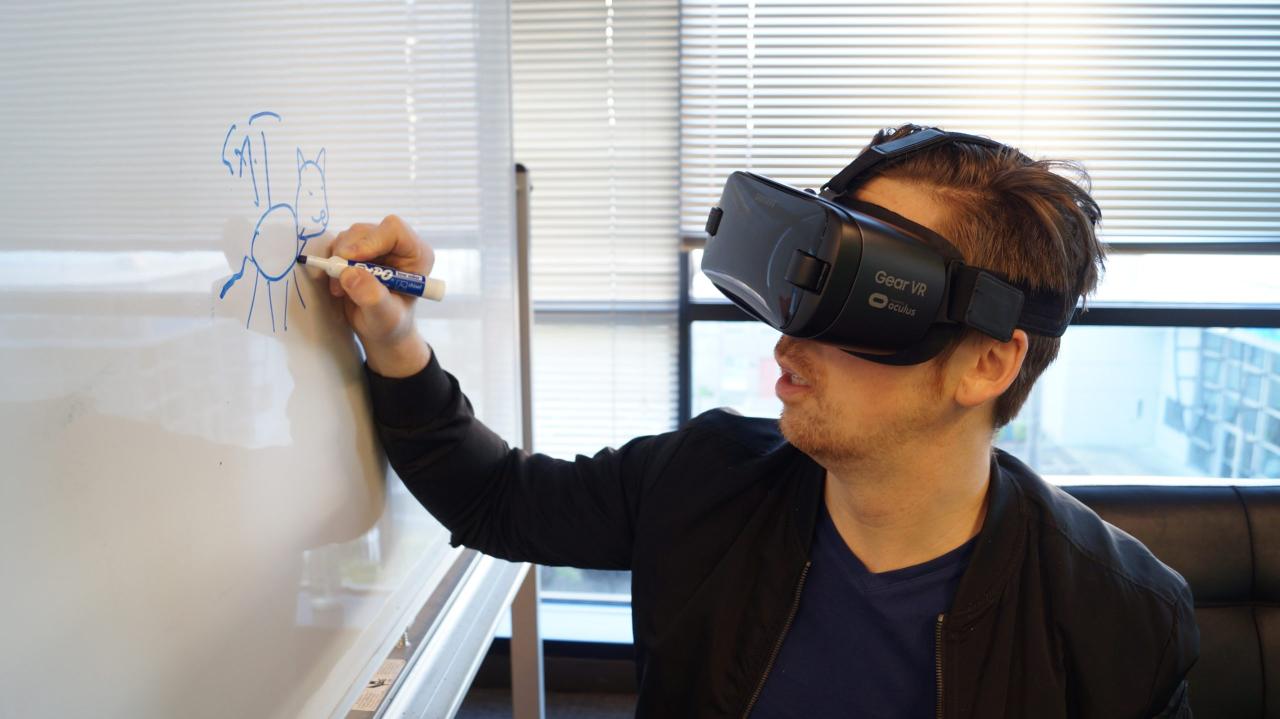
VR Career Simulations for Job Training represent a revolutionary approach to equipping individuals with the skills and experience necessary for today’s dynamic job market. By immersing users in realistic workplace scenarios, these simulations facilitate experiential learning that traditional training methods often lack. As industries continuously evolve, the integration of virtual reality into career preparation not only enhances engagement but also addresses the gaps in practical experience that many job seekers face.
The significance of these simulations extends beyond mere skill acquisition; they foster an environment where learners can practice critical thinking, problem-solving, and interpersonal skills in a risk-free setting. This innovative training modality is gaining traction across various sectors, highlighting its potential to redefine how we approach job training in an increasingly digital world.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has evolved significantly since its inception in the mid-20th century. The journey of AI is characterized by remarkable advancements, shifts in paradigms, and a growing impact on various sectors. This article examines the historical milestones, current trends, and future potential of AI, highlighting the technology’s transformative role in society.
Historical Context: VR Career Simulations For Job Training
The origins of AI can be traced back to the 1950s, when pioneers like Alan Turing and John McCarthy laid the groundwork for computational intelligence. Turing’s seminal paper, “Computing Machinery and Intelligence,” proposed the concept of a machine capable of intelligent behavior, introducing the famous Turing Test as a measure of a machine’s ability to exhibit human-like intelligence. In 1956, McCarthy organized the Dartmouth Conference, which is considered the birthplace of AI as a formal field of study.
The decades that followed saw the development of early AI programs, such as the Logic Theorist and the General Problem Solver, which demonstrated the potential for machines to engage in logical reasoning. However, progress was slow, and the field faced numerous challenges, leading to periods known as “AI winters,” where funding and interest waned due to unmet expectations.
Key Milestones in AI Development
The resurgence of AI began in the late 1990s and early 2000s, driven by advancements in computational power and the availability of large datasets. Some key milestones during this period include:
- Deep Blue (1997): IBM’s chess-playing computer defeated world champion Garry Kasparov, showcasing the potential of AI in strategic games.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): The development of algorithms like Latent Semantic Analysis and advancements in machine learning techniques improved the ability of machines to understand and process human language.
- Image Recognition: The advent of deep learning techniques, particularly convolutional neural networks (CNNs), revolutionized image processing, leading to significant improvements in facial recognition and object detection.
The Rise of Machine Learning and Deep Learning
One of the most significant developments in AI is the rise of machine learning (ML) and, more specifically, deep learning (DL). Machine learning, a subset of AI, involves algorithms that enable computers to learn from data and improve their performance over time without explicit programming. Deep learning, a further subset of ML, employs artificial neural networks with multiple layers to analyze complex patterns in data.
Deep learning has driven breakthroughs in various applications, including:
- Healthcare: AI systems are being used to analyze medical images, predict patient outcomes, and assist in drug discovery.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Companies like Tesla and Waymo leverage deep learning for perception, decision-making, and navigation in self-driving cars.
- Virtual Assistants: AI-driven virtual assistants, such as Siri and Alexa, utilize natural language processing and machine learning to understand and respond to user queries.
Current Trends in AI
As AI continues to evolve, several current trends are shaping the landscape:
1. AI Ethics and Governance
With the increasing deployment of AI systems, ethical considerations surrounding bias, accountability, and transparency have gained prominence. Organizations are recognizing the need for frameworks to ensure AI is used responsibly, leading to the establishment of AI ethics boards and guidelines.
2. Explainable AI
The demand for transparency in AI decision-making has led to the development of explainable AI (XAI). XAI aims to create models that offer insights into their decision processes, allowing users to understand how conclusions are reached, which is particularly important in high-stakes domains like healthcare and finance.
3. AI in Business and Automation
Businesses are increasingly adopting AI for process automation, predictive analytics, and customer service enhancements. AI-driven chatbots, for example, are streamlining customer interactions, while predictive maintenance algorithms are optimizing manufacturing processes.
4. AI and the Workforce
The rise of AI has sparked debates about the future of work. While automation threatens certain job roles, it also creates opportunities for new positions in AI development, data science, and machine learning engineering. Reskilling and upskilling the workforce will be crucial to navigating this transition.
The Future of AI
Looking ahead, the future of AI appears promising yet complex. Several potential trends and developments could shape the next phase of AI evolution:
1. General Artificial Intelligence (AGI)
The pursuit of artificial general intelligence (AGI), where machines possess the ability to understand, learn, and apply knowledge across a wide range of tasks at a human level, remains an ongoing challenge. While significant progress has been made in narrow AI, achieving AGI will require breakthroughs in cognitive architectures, learning methodologies, and ethical considerations.
2. AI and Human Collaboration, VR Career Simulations for Job Training
The concept of human-AI collaboration is gaining traction, with the belief that AI can augment human capabilities rather than replace them. This partnership could lead to enhanced creativity, decision-making, and problem-solving in various fields.

3. Regulation and Policy Frameworks
As AI technologies become more pervasive, regulatory frameworks will be essential to govern their use. Policymakers must address issues related to privacy, security, and the ethical implications of AI to protect individuals and society.
4. AI in Climate Change Mitigation
AI holds significant potential in addressing global challenges such as climate change. From optimizing energy consumption to enhancing climate modeling and forecasting, AI can play a crucial role in developing sustainable solutions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the evolution of artificial intelligence has been marked by significant milestones, technological advancements, and an increasing presence in everyday life. As AI continues to evolve, it is imperative to address the ethical, societal, and regulatory challenges that accompany its growth. The future of AI is not just about technological progress; it is also about ensuring that these advancements contribute positively to humanity and the world at large.
Through collaborative efforts between researchers, policymakers, and the private sector, the transformative potential of AI can be harnessed responsibly, paving the way for a future where human and artificial intelligence coexist and thrive together.