Agriculture and BI: Data-Driven Farming is transforming how we approach food production and resource management. With the rapid advances in technology, farmers are increasingly leveraging data analytics to make informed decisions that boost productivity and sustainability. This intersection of agriculture and business intelligence not only enhances crop yields but also optimizes supply chains, making farming more efficient than ever before.
This evolution in farming practices signifies a shift toward smarter agriculture, where data-driven insights are key to addressing the challenges of modern farming. By utilizing various data sources, from climate patterns to soil health, farmers can tailor their strategies to environment and market demands, ensuring both profitability and ecological responsibility.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has transitioned from being a mere concept in science fiction to a significant component of our everyday lives. From the smartphones we carry to the sophisticated algorithms that drive services like Netflix and Spotify, AI is reshaping how we interact with technology. This article delves into the depths of AI, its applications, benefits, challenges, and the future it holds.
Understanding Artificial Intelligence
At its core, AI refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines programmed to think and learn. These systems can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as visual perception, speech recognition, decision-making, and language translation. The fundamental goal of AI is to create systems that can function intelligently and independently.
Types of Artificial Intelligence: Agriculture And BI: Data-Driven Farming
AI can be classified into two main categories:
- Narrow AI: Also known as weak AI, this type is designed to perform a narrow task (e.g., facial recognition or internet searches). Most of the AI we encounter today is narrow AI.
- General AI: This type, also known as strong AI, would outperform humans at nearly every cognitive task. However, we are yet to achieve this level of AI.
Applications of Artificial Intelligence
The applications of AI are diverse and continually expanding. Here are some notable areas where AI has made a significant impact:
Healthcare
AI is revolutionizing the healthcare sector by improving diagnostics, personalizing treatment plans, and managing hospital resources efficiently. Machine learning algorithms analyze medical data to identify patterns and predict patient outcomes, leading to more accurate diagnoses and tailored treatments.
Transportation
Self-driving cars are perhaps one of the most exciting applications of AI in transportation. Companies like Tesla and Waymo are developing vehicles equipped with AI systems that can navigate traffic, recognize obstacles, and make real-time decisions, thus enhancing safety and efficiency on the roads.
Finance
AI is transforming the finance industry by enabling improved fraud detection, risk management, and customer service. Algorithms analyze transaction patterns to detect anomalies, while chatbots provide instant customer support, enhancing user experience.
Entertainment, Agriculture and BI: Data-Driven Farming
Streaming services utilize AI algorithms to analyze viewer preferences and recommend content tailored to individual tastes. This personalization significantly enhances user engagement and satisfaction.
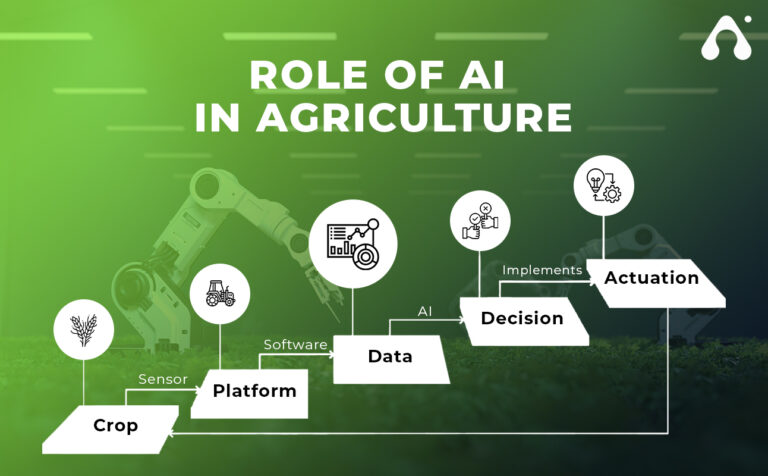
The Benefits of Artificial Intelligence
AI offers numerous benefits across various sectors:
- Efficiency: Automation of repetitive tasks allows organizations to allocate resources more effectively.
- Data Analysis: AI can process vast amounts of data quickly, uncovering insights that might take humans much longer to discover.
- 24/7 Availability: Unlike humans, AI systems can operate around the clock, providing services without breaks.
- Improved Decision Making: By analyzing data and predicting outcomes, AI can assist in making informed decisions swiftly.
Challenges Facing Artificial Intelligence
Despite its many advantages, AI also poses challenges that need to be addressed:
Ethical Concerns
AI raises significant ethical issues, such as bias in algorithms, privacy concerns, and the potential for job displacement. Ensuring that AI systems operate fairly and transparently is crucial for public trust.
Security Risks
As AI systems become more prevalent, they also become targets for malicious attacks. Ensuring the security of AI applications is vital to prevent misuse and protect sensitive information.
Dependence on Technology
Increased reliance on AI might lead to a decline in critical thinking and problem-solving skills among humans. Striking a balance between leveraging AI and maintaining human skills is essential.
The Future of Artificial Intelligence
The future of AI is promising, with ongoing advancements in technology. Here are some trends to watch:
- Explainable AI: As AI systems become more complex, there’s a growing demand for transparency in how they make decisions.
- AI in Everyday Life: AI will increasingly integrate into daily routines, enhancing convenience and efficiency in tasks ranging from home management to personalized shopping experiences.
- Collaboration with Humans: The future of work will likely involve collaboration between humans and AI, where machines assist humans in decision-making rather than replacing them entirely.
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence is not just a technological trend; it is a transformative force that is reshaping industries and daily life. While the journey of AI is laden with challenges, the potential benefits and opportunities for innovation are immense. As we continue to explore and expand the frontiers of AI, it becomes paramount to navigate the ethical landscape and ensure that this powerful tool is harnessed for the betterment of society.
The future holds exciting possibilities, and it is up to us to steer AI development towards a positive outcome for all.